Brief Computer Task May Prolong Effects of Ketamine
Abstract
The ASAT computer program trains people to perceive themselves in a more positive light during the time when ketamine is believed to make the brain more receptive to processing new information.
Completing a brief computer program that aims to boost self-esteem may extend the antidepressant effects of a single ketamine infusion for at least 30 days, a report in The American Journal of Psychiatry has found.
Ketamine’s rapid antidepressant effects offer “the promise of a breakthrough in the way depression is managed, but this promise remains unfulfilled to date,” wrote lead author Rebecca B. Price, Ph.D., an associate professor of psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, and colleagues. “Quickly dissipating effects after a single infusion in isolation, coupled with substantial concerns regarding the safety and feasibility of repeated infusions, limit ketamine’s clinical impact.”
While ketamine’s exact mechanisms remain uncertain, there is evidence that this drug can temporarily enhance neural plasticity (the ability of neurons to form new and different connections). Thus, in the first few days following an infusion, the brain may be “primed” to change to a healthier state.
To test this, Price and colleagues paired ketamine treatment with a computer program called automated self-association training (ASAT). This program uses cognitive tasks to condition people to associate thoughts about themselves with positive feelings, in essence improving self-worth.
As Price explained to Psychiatric News, such cognitive training tools have been shown to improve body image, so a modified tool focused on depressive thoughts could work as well.
In total, 154 adults (aged 18 to 60) with treatment-resistant depression were assigned to one of three treatment protocols:
One group received a single ketamine infusion (0.5 mg/kg over 40 minutes) plus ASAT.
One group received a saline infusion plus ASAT.
One group received a ketamine infusion plus sham ASAT.
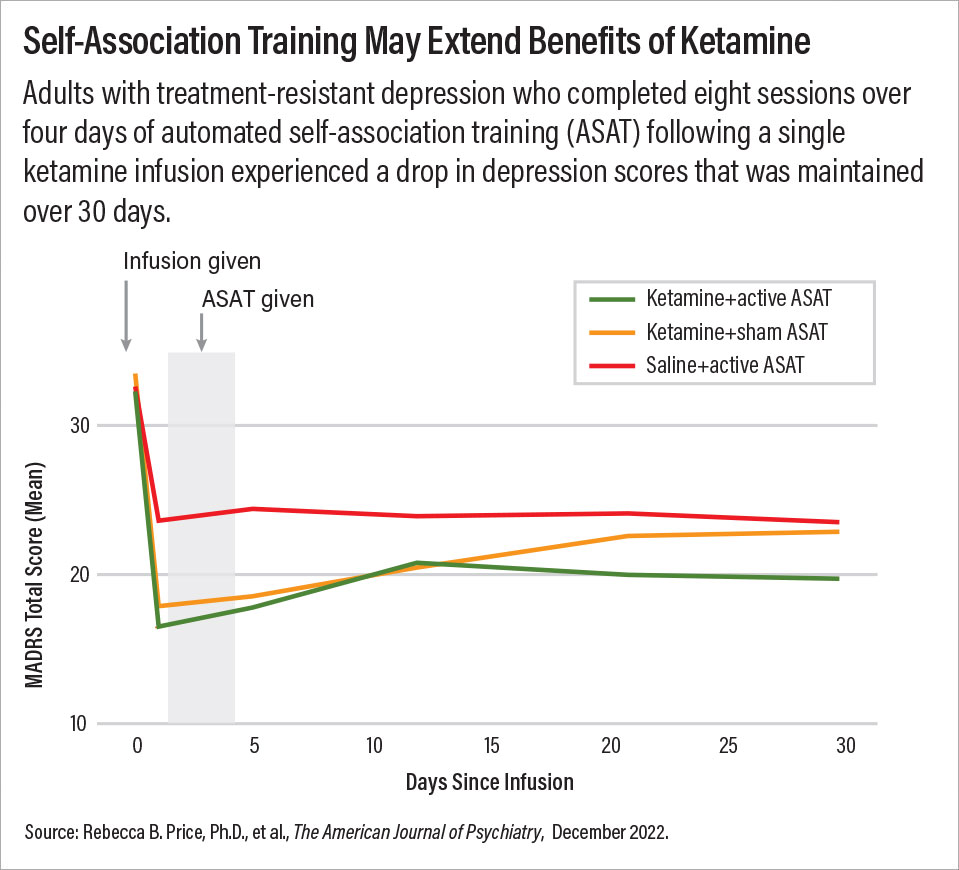
Both ASAT and sham ASAT consisted of eight 15- to 20-minute sessions delivered twice daily for four consecutive days starting one day after the infusion. For the ASAT sessions, participants completed computer tasks that featured words associated with positive feelings (such as “lovable” and “worthy”) and images of themselves and other people. The sham ASAT consisted of the same computer tasks, but with predominantly neutral images and words and no references to the participant.
The participants’ depressive symptoms were assessed using the clinician-administered Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) multiple times over the course of the 30-day study.
As anticipated, symptoms improved significantly more after 24 hours among adults who received a ketamine infusion; 52% of adults who received ketamine achieved a treatment response (at least 50% reduction in MADRS scores) compared with 25% of adults who received saline. Depression scores in the ketamine plus ASAT group remained low and stable for 30 days compared with those in the saline plus ASAT group. In contrast, depression scores in the ketamine plus sham ASAT group increased after 24 hours.
Interestingly, depression scores also remained lower for 30 days among adults who received saline plus ASAT. However, Price told Psychiatric News that since this study did not have a true control group (saline plus sham training), it remains unknown whether these reductions point to a beneficial effect of ASAT even in ketamine’s absence. “The improvements could be due to nonspecific factors like the pleasant interactions participants had with our research staff,” she said.
Price also cautioned that while ASAT’s concept of pairing positive emotions with self-perception seems simple, the program tasks were very systematic. “I don’t want people to think they can look at happy magazine photos and achieve a similar effect,” she said. “This was also a preliminary study that needs to be replicated.”
Still, tools like ASAT could potentially offer an accessible and low-cost way to sustain critical depression relief. She noted her team is currently testing a phone/tablet-based version of ASAT in an inpatient setting. “If those results are promising, the next logical step would be to test ASAT in real-world clinics that offer ketamine and esketamine therapy.”
This study was supported by a Biobehavioral Research Award from the National Institute of Mental Health as well as a grant from the Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute at the University of Pittsburgh. ■



