Depression Remission After SSRI Linked to Gene Variations
New analyses of the Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR*D) study data suggest that remission of depressive symptoms after treatment with citalopram is significantly associated with certain genetic variations in DNA segments that regulate the expression of the serotonin transporter gene SLC6A4.
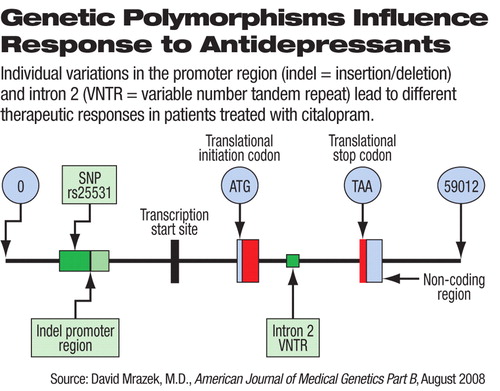
The researchers, whose study appeared in the August American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B, examined the genetic data from 1,074 white, non-Hispanic patients; 196 white Hispanic patients; and 233 black non-Hispanic patients, based on self-reported race and ethnicity. They all had participated in the STAR*D study, conducted from 2001 to 2006. The three groups were separately analyzed to identify any associations between genetic variations in the SLC6A4 gene and remission from depression.
Among white non-Hispanic patients in the study, remission was significantly associated with two specific variations: the variable number of tandem repeats variation in the second intron and the insertion/deletion polymorphism in the promoter region. However, these variations were not significantly associated with remission in white Hispanic patients and black patients.
Three genetic variations were investigated in this study, all of which are located in the noncoding region of SLC6A4. These variations have been implicated in regulating the expression of the serotonin transporter gene. The third polymorphism studied, a single nucleotide polymorphism known as rs25531, was not found to be statistically significantly associated with remission.
The findings add pieces to the puzzle of the interactions among genes, depression, and treatment response, although scientists are still a long way from seeing the whole picture.
“There has been a lot of research into the SLC6A4 gene in depression, and some of these studies did not find significant association with response,” David Mrazek, M.D., chair of the Department of Psychiatry and Psychology at the Mayo Clinic, told Psychiatric News. He noted that this study gave further confirmation that genetic variations have a significant role in determining patients' response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Mrazek, a member of APA's Council on Children, Adolescents, and Their Families, commented that the racial and ethnic differences in the genetic associations observed in this study may explain the negative findings in some of the past studies. For example, studies conducted in Europe with a predominantly Caucasian population tended to find a statistically significant association between the SLCA64 polymorphisms and treatment response, but studies conducted in racially mixed populations had equivocal results.
“It is important to realize that the genetic association to clinical response is not generalizable to patients of [non-white] racial and ethnic groups,” said Mrazek. The reason for this phenomenon remains unknown.
The authors also investigated the interactions among all three alleles and found that a certain combination of polymorphisms had the lowest probability of remission, which suggested that genetic-based prediction of response to treatment would be more informative if a patient is genotyped for several key alleles. “As we learn more about the regulatory mechanisms of gene expression, we will be able to define a continuous spectrum for the clinical outcome in a patient,” Mrazek said. Depending on the actual versions of more than one important allele carried by a person, scientists may be able to predict with greater certainty how likely he or she will respond to a treatment.
An abstract of “SLC6A4 Variation and Citalopram Response” is posted at<www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/120750232/abstract>.▪



